
Involving velocity, pressure, density and temperature as functions of space and time.
#GLYCEROL WATER VISCOSITY FREE#
The molar enthalpy (H), entropy (S) and Gibbs free energy of activation (G) of viscosity were calculated. It has been interpreted that strong interaction for the sulfolane + system, meanwhile weak interaction was deduced for the sulfolane + glycerol system. Quantum chemical based COSMO-RS was used to predict the molecular interaction and non-ideal liquid phase activity coefficient for all mixtures.
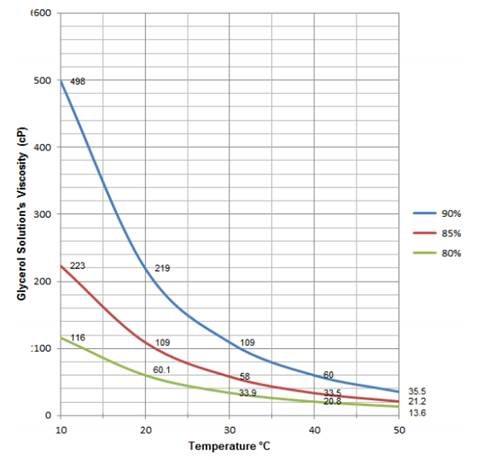
The predicted values were close to the corresponding experimental data with all the standard deviation lower than 1 × 10 −3. From these experimental values, thermal expansion (), excess molar volume (V E), viscosity deviation () and Gibbs free energy (G) were calculated. In this context, density () and viscosity () of sulfolane with glycerol and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide have been measured over the entire range of composition with temperature ranging from 298.15 K to 363.15 K at atmospheric pressure. But in the absence of experimental data, an accurate predictive method is required. Thermophysical properties of solvent are set of data that are essential for designing processes in industry. A critical volume concentration of 0.5% and 1% were observed with respect to the electrical conductivity increase with volume concentration for 3 h and 6 h samples respectively, after which a reduction to plateu was prominent which signifies counter-ion condenstation. Comparing the experimental data with the available low volume concentration classical models and emipiral model revealed that the classical models under predicted our experimental data, while, the empirical model anormalously over predicted the experimental data reported in this work. However, 6 h sonication effect was only felt at the reduction of the relative viscosity of 2% volume concentration, with the critical temeprature observed at 55 o C for all volume fractions.
In the case of 3 h samples, the study shows no appreciable increase in the relative viscosity up to 0.5% nanoparticles volume concentration and it was observed to reach a critical vlaue (beyond which the relative viscosity starts reducing with temperature) at 55 o C for 2%, 60 o C for 1% and 65 o C for both 0.5% and 0.1% volume concentrations respectively. The effect of volume concentration on the effective viscosity, electrical conductivity and pH were all monitored between the temperature range of 20–70 o C. Stable -Al 2 O 3 –glycerol nanofluids samples were prepared using the famous two-step method, followed by ultrasonication at two different time period of 3 h and 6 h in a controlled temperature bath. This was accomplished by studying the effect of the two most basic parameters, namely temperature and volume concentration at constant shear rate on 20–30 nm -Al 2 O 3 in glycerol. In this study, the viscosity of -Al 2 O 3 – glycerol nanofluids a prime factor in the design of heat tranfer equipment such as heat exchanger has been investigated in the Einstein's volume concentration regime ( ≤ 2%). In recent times, nanofluids have shown a great promise of bringing about sustainable energy development in the field of heat transfer and regarding the design of heat transfer equipment. Energy sustainability is very crucial for any viable engineering solution to be achieved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
